430. Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
Leetcode Linked List Depth-First SearchYou are given a doubly linked list which in addition to the next and previous pointers, it could have a child pointer, which may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure, as shown in the example below.
Flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. You are given the head of the first level of the list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6]
Explanation:
The multilevel linked list in the input is as follows:
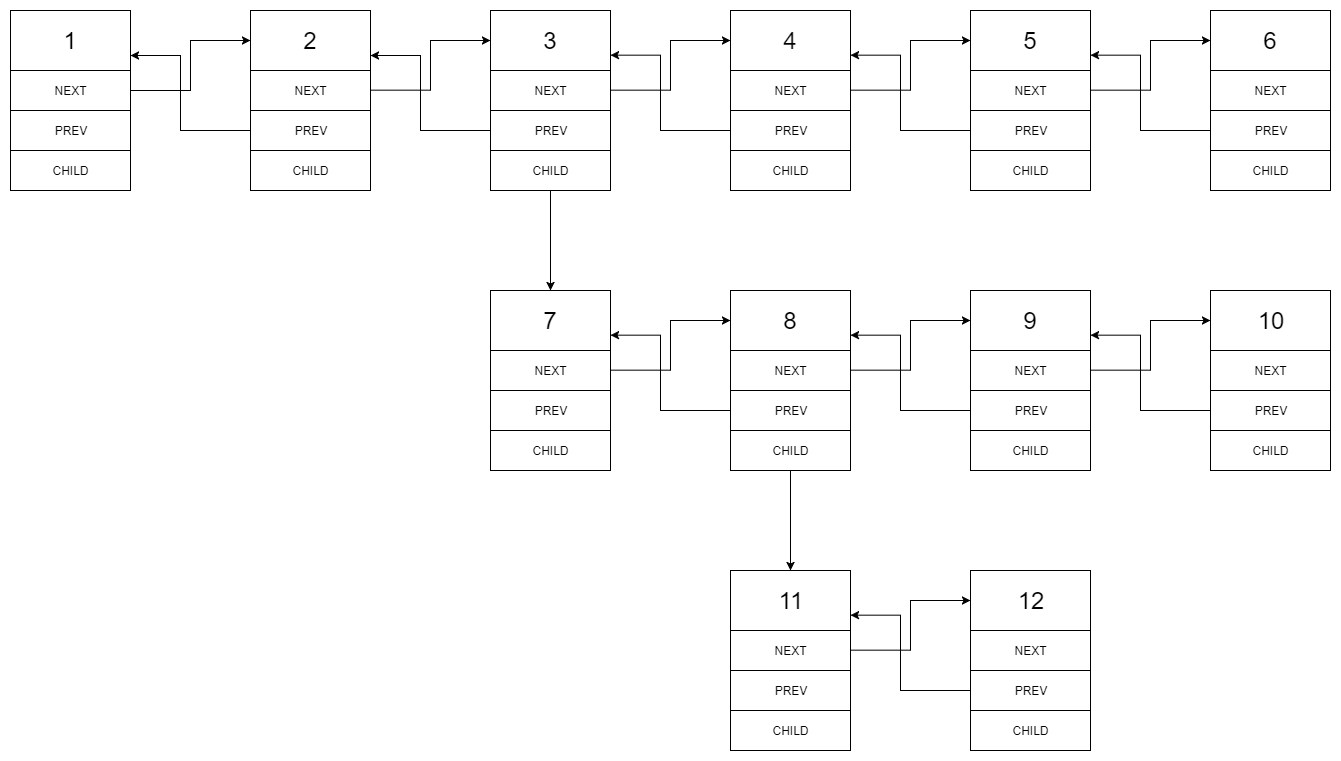
After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes:

Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,null,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Explanation:
The input multilevel linked list is as follows:
1---2---NULL
|
3---NULL
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
How multilevel linked list is represented in test case:
We use the multilevel linked list from Example 1 above:
1---2---3---4---5---6--NULL
|
7---8---9---10--NULL
|
11--12--NULL
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null]
[7,8,9,10,null]
[11,12,null]
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null]
[null,null,7,8,9,10,null]
[null,11,12,null]
[1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12]
Constraints:
- Number of Nodes will not exceed 1000.
1 <= Node.val <= 10^5
分析¶
根据这道题目的意思,把链表拉平就意味着在遍历链表时,如果遇到子链表(child != null),则优先遍历子链表。遍历完所有子链表之后,回来遍历剩下的链表。可以用栈保存暂时还未遍历的链表。
java
public Node flatten(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
// 遍历链表
Node root = new Node(), cur = root, prev = root;
while (head != null) {
cur.next = head;
cur.child = null;
head.prev = cur;
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
// 如果有子链表,先保存到栈中
if (head.child == null) {
head = head.next;
} else {
stack.push(head.next);
head = head.child;
}
}
// 遍历栈中的链表
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Node node = stack.pop();
while (node != null) {
cur.next = node;
node.prev = cur;
node = node.next;
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
cur.prev = prev;
// 别忘了,把链表头节点的prev设置为null
root.next.prev = null;
return root.next;
}