17 Protection
1 Goals of Protection¶
Protection was originally conceived as an adjunct to multiprogramming operating system,
- to allow untrustworthy users to safely share a common logical name space, such as a directory files, or a common physical name space, such as memory.
Modern protection,
- to increase the reliability of any complex system that makes use of shared resources and is connected to insecure communications platforms such as Internet.
Protection are needed for several reasons.
- Preventing the mischievous, intentional violation of an access restriction by a user is needed.
- Protection can improve reliability by detecting latent errors at the interfaces between component subsystems.
- provide a mechanism for the enforcement of the policies governing resource use
3 Protection Rings¶
To carry out privilege separation, hardware support is required. A popular model of privilege separation is that of protection rings(保护环) or hierarchical protection domains(分级保护域). In this model, execution is defined as a set of concentric rings, with ring i providing a subset of the functionality of ring j for any j < i. The innermost ring, ring 0, thus provides the full set of privileges.
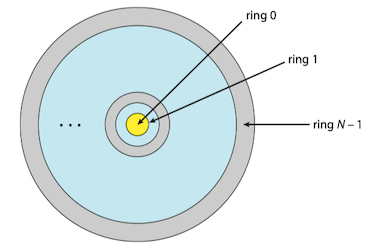
X86 CPU ring
The x86-processors have four different modes divided into four different rings.
- Ring 0: kernels and drivers
- Ring 1: device drives, also used for virtualization
- Ring 2: device drives
- Ring 3: application programs
It is implemented by two bits in the special EFLAGS register. Access to this register is not allowed in ring 3 — thus preventing a malicious process from escalating privileges.
