Maven
JavaMaven是一个构建工具,可以自动管理依赖,源代码编译,测试编译,测试执行。
1 POM文件¶
Pom.xml文件放在工程跟目录下,包含了关于工程和配置的详细信息。Maven使用这些信息构建工程。
配置¶
具体的配置说明,详见官网POM Reference。下面是一个常见POM文件的内容:
第一部分,项目坐标,信息描述等
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.company.project</groupId>
<artifactId>module</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>test Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
- modelVersion:pom文件的模型版本
- group id:com.公司名.项目名
- artifact id:功能模块名
- packaging:项目打包的后缀,war是web项目发布用的,默认为jar
- version: artifact模块的版本
- name和url:相当于项目描述,可删除
- group id + artifact id +version :项目在仓库中的坐标
第二部分, 依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-csv</artifactId>
<version>1.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
上面引入了Apache commons csv项目,可以在官网找到Maven设置。
- dependency:引入资源jar包到本地仓库,要引入更多资源就在
中继续增加 - group id+artifact id+version:资源jar包在仓库中的坐标
- scope:作用范围,test指该jar包仅在maven测试时使用,发布时会忽略这个包。需要发布的jar包可以忽略这一配置
第三部分,构建项目
<build>
<finalName>helloworld</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.7</source>
<target>1.7</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
- build:项目构建时的配置
- finalName:在浏览器中的访问路径,如果将它改成helloworld,再执行maven--update,这时运行项目的访问路径是 http://localhost:8080/helloworld/, 而不是项目名的 http://localhost:8080/test
- plugins:插件
- group id+artifact id+version:插件在仓库中的坐标
- configuration:设置插件的参数值
属性¶
可以在properties节点下自定义属性<property1>value1</property1>,以${property1}的形式引用它们。
<properties>
<test.uuid>123</test.uuid>
<jdbc.driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</jdbc.driverClassName>
<hadoop.version>2.7.7</hadoop.version>
</properties>
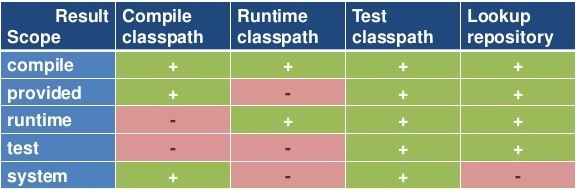
依赖范围¶
| scope | 说明 |
|---|---|
| compile | 默认的范围;如果没有提供一个范围,那该依赖的范围就是编译范围。编译范围依赖在所有的classpath 中可用,同时它们也会被打包 |
| provided | 依赖只有在当JDK 或者一个容器已提供该依赖之后才使用。例如, 如果你开发了一个web 应用,你可能在编译 classpath 中需要可用的Servlet API 来编译一个servlet,但是你不会想要在打包好的WAR 中包含这个Servlet API;这个Servlet API JAR 由你的应用服务器或者servlet 容器提供。已提供范围的依赖在编译classpath (不是运行时)可用。它们不是传递性的,也不会被打包。 |
| runtime | 依赖在运行和测试系统的时候需要,但在编译的时候不需要。比如,你可能在编译的时候只需要JDBC API JAR,而只有在运行的时候才需要JDBC驱动实现。 |
| test | test范围依赖 在一般的编译和运行时都不需要,它们只有在测试编译和测试运行阶段可用 |
| system | system范围依赖与provided 类似,但是你必须显式的提供一个对于本地系统中JAR 文件的路径。这么做是为了允许基于本地对象编译,而这些对象是系统类库的一部分。这样的构件应该是一直可用的,Maven 也不会在仓库中去寻找它。如果你将一个依赖范围设置成系统范围,你必须同时提供一个 systemPath 元素。注意该范围是不推荐使用的(你应该一直尽量去从公共或定制的 Maven 仓库中引用依赖) |
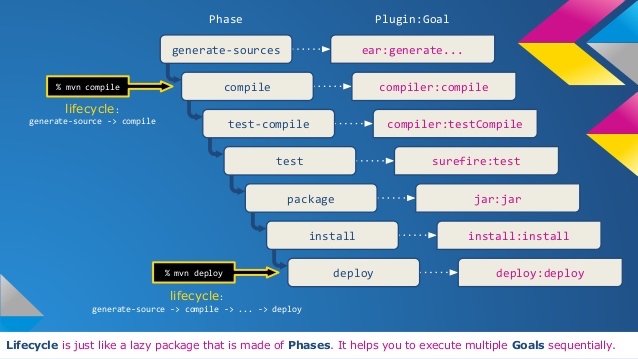
2 生命周期¶
Maven中的每个执行工作单元被称为goal
打包¶
Maven提供的打包插件有多种,具体目录见官网。下面讲解一下最常见的几种。
| 插件 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| maven-jar-plugin | maven 默认打包插件,用来创建 project jar |
| maven-shade-plugin | 用来打可执行包,executable(fat) jar |
| maven-assembly-plugin | 支持定制化打包方式,例如 apache 项目的打包方 |
maven-jar-plugin¶
该插件为pom默认的打包插件。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<configuration>
<outputDirectory>${basedir}</outputDirectory>
</configuration>
</plugin>
maven-shade-plugin¶
详见官网:http://maven.apache.org/plugins/maven-shade-plugin/usage.html
通过maven-shade-plugin生成一个 uber-jar,它包含所有的依赖 jar 包。也可以使用该插件解决包冲突问题。
下面的配置将org.codehaus.plexus.util的jar包重命名为 org.shaded.plexus.util。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<relocations>
<relocation>
<pattern>org.codehaus.plexus.util</pattern>
<shadedPattern>org.shaded.plexus.util</shadedPattern>
<!--指定哪些依赖不需要打包-->
<excludes>
<exclude>org.codehaus.plexus.util.xml.Xpp3Dom</exclude>
<exclude>org.codehaus.plexus.util.xml.pull.*</exclude>
</excludes>
</relocation>
</relocations>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
maven-assembly-plugin¶
将相关文件打包一起分发出去,常见的例如apache的分发包以及常用的zip等包信息。配置说明:
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<configuration>
<classifier>dist</classifier>
<appendAssemblyId>true</appendAssemblyId>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptor>jar-with-dependencies</descriptor>
</descriptorRefs>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>${package_name}.Main</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assembly</id> <!-- this is used for inheritance merges -->
<phase>package</phase> <!-- bind to the packaging phase -->
<goals>
<goal>single</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
java与scala混合打包¶
使用maven-scala-plugin将java和scala一起打包。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.scala-tools</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-scala-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.15.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>scala-compile-first</id>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<includes>
<include>**/*.scala</include>
</includes>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
3 目录结构¶
Maven有一个标准的目录结构。如果你在项目中遵循Maven的目录结构,就无需在pom文件中指定源代码、测试代码等目录。
- src
- main
- java
- resources
- webapp
- test
- java
- resources
- target
- src目录是源代码和测试代码的根目录
- main目录是应用的源代码目录
- test目录是测试代码的目录
- main和test下的java目录,分别表示应用的java源代码和测试代码。
- resources目录包含项目的资源文件,比如应用的国际化配置的属性文件等。
- 如果是一个web项目,则webapp目录为web项目的根目录,其中包含如WEB-INF等子目录。
- target目录是由Maven创建的,其中包含编译后的类文件、jar文件等。当执行maven的clean目标后,target目录会被清空。
4 Maven仓库¶
Maven仓库就是存储jar包和一些元数据信息的目录。其中的元数据即pom文件,描述了该jar包属于哪个项目,以及jar包所需的外部依赖。该元数据信息使得Maven可以递归地下载所有的依赖,直到整个依赖树都下载完毕并放到你的本地仓库中。Maven有三种类型的仓库:本地仓库(local)、中央仓库(central)、远程仓库(remote)。
本地仓库¶
Maven的本地仓库默认在$HOME/.m2/repository。该仓库包含了Maven下载的所有依赖。一般来讲,一个本地仓库为多个不同的项目服务。因此,Maven只需下载一次,即使有多个项目都依赖它。其包含配置文件settings.xml,可以在其中指定本地仓库为其它的路径:
<settings>
<localRepository>\data\java\products\maven\repository</localRepository>
</settings>
通过mvn install命令可以将你自己的项目构建并安装到本地仓库中。这样,你的其它项目就可以通过在pom文件将该jar包作为外部依赖来使用。
# example
mvn install:install-file -Dfile=/lib/ipdatabase-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar \
-DgroupId=com.ggstar -DartifactId=ipdatabase -Dversion=1.0 -Dpackaging=jar
# 如果也有pom文件的话,你可以使用下面的命令安装:
mvn install:install-file -Dfile= -DpomFile=
中央仓库¶
Maven的中央仓库由Maven社区提供。默认情况下,所有不在本地仓库中的依赖都会去这个中央仓库查找。然后Maven会将这些依赖下载到你的本地仓库。访问中央仓库不需要做额外的配置。如果想覆盖中央仓库的默认地址,可以在$M2_HOME/setting.xml里面配置:
<mirror>
<id>alimaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
</mirror>
一般推荐以下Maven中央仓库地址:
- http://mvnrepository.com/
- https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public
远程仓库¶
远程仓库是位于web服务器上的一个仓库,Maven可以从该仓库下载依赖,就像从中央仓库下载依赖一样。远程仓库可以位于Internet上的任何地方,也可以是位于本地网络中。远程仓库一般用于放置组织内部的项目,该项目由多个项目共享。比如,由多个内部项目共用的安全项目。该安全项目不能被外部访问,因此不能放在公开的中央仓库下,而应该放到内部的远程仓库中。
可以在pom文件里配置远程仓库:
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>jenkov.code</id>
<url>http://maven.jenkov.com/maven2/lib</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
仓库切换¶
如果希望使用阿里云镜像,如下执行:
mvn help-effective-settings -Daliyun=central
5 其他¶
多线程¶
指明多线程进行编译:-Dmaven.compile.fork=true