15 File System Internals
1 File Systems¶
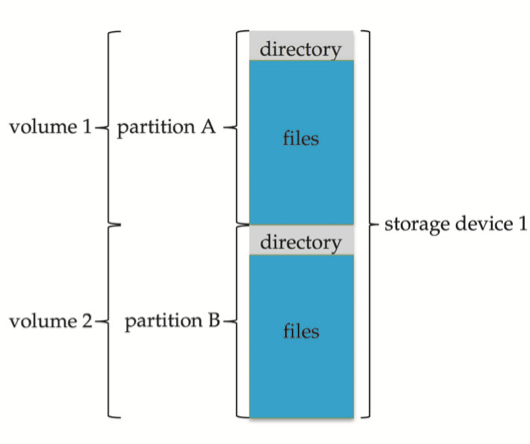
Storage Devices can be sliced up into partitions, which hold volumes, which in turn hold file systems. A typical storage device organization:
2 File-System Mounting¶
A file system must be mounted before it can be available to processes on the system:
- given the name of the device and the mount point(the location within the file structure where the file system is to be attached).
- verifies that the device contains a valid file system, by asking the device driver to read the device directory and verifying that the directory has the expected format.
- mounted at the specified mount point.
5 Virtual File Systems¶
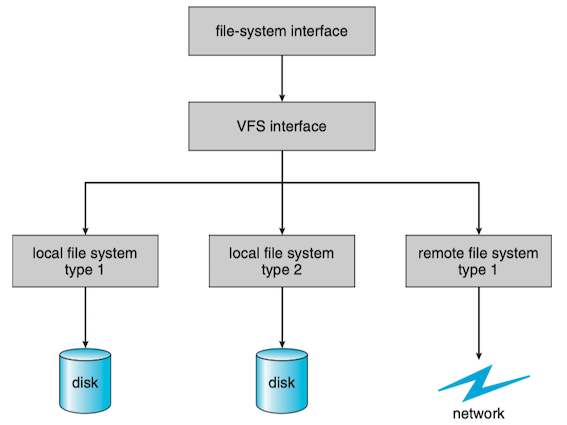
ISSUE: How does an operating system allow multiple types of file systems to be integrated into a directory structure? And how can users seamlessly move between file-system types as they navigate the file-system space?
SOLUTION: virtual file system (VFS, 虚拟文件系统) layer which services two important functions:
- separates file-system-generic operations from their implementation by defining a clean VFS interface.
- provides a mechanism for uniquely representing a file throughout a network.
- the VFS is based on a file-representation structure, called a vnode, that contains a numerical designator for a network-wide unique file. (UNIX inode are unique within only a single file system)
The file-system implementation consists of three major layers:
- file-system interface: based on the
open(),read(),write()andclose()calls and on file descriptors - virtual file system (VFS) layer
- local/remote file system
The four main object types defined by the Linux VFS are:
- inode (index node): represents an individual file
- file object: represents an open file
- superblock: represents an entire file system. It is essentially file system metadata and defines the file system type, size, status, and information about other metadata structures (metadata of metadata).
- dentry(directory entry): represents an individual directory entry